RAK ICC Foundation

RAK ICC Foundation
The RAK International Corporate Centre (RAK ICC) Foundations serve as corporate entities with a distinct legal personality that separates them from their founders. These Foundations are expertly managed by a council, which is responsible for administering assets and fulfilling the Foundation's objectives.
Uses of RAK ICC Foundations:
- Strengthened succession planning and asset protection.
- Establishing a robust governance structure
- Implementing guardian oversight
- Creating a distinct legal personality that effectively separates liability while maintaining control over assets, ensuring perpetual existence beyond the founder's lifetime
- Strategically holding assets
- Distributing dividends from operating companies with precision
- Holding shares in RAK ICC companies
- Managing and securing the founder's assets for the benefit of qualified recipients
- Overseeing operating companies
- Advancing family philanthropic initiatives with purpose
Key Advantages of RAK ICC Foundations:
- International Compliance: Operates within a registry that meets global standards.
- Strong Governance Structure: Establishes a solid framework for decision-making and oversight.
- Favourable Tax Environment: Benefits from an attractive tax regime in the UAE.
- Simplicity in Compliance: No requirement for annual filing or auditing, while ensuring adherence to RAK ICC Anti-Money Laundering requirements as outlined in the RAK ICC Business Companies Regulations 2018.
- Migration Flexibility: Provides the option to seamlessly transition from other jurisdictions to RAK ICC.
- Cost-Effective Administration: Features low registration and administrative fees.
- Perpetual Governance Options: Allows for governance models designed for ongoing operation and sustainability.
- Beneficiary Flexibility: Supports a diverse range of beneficiary classes, accommodating various needs and objectives.
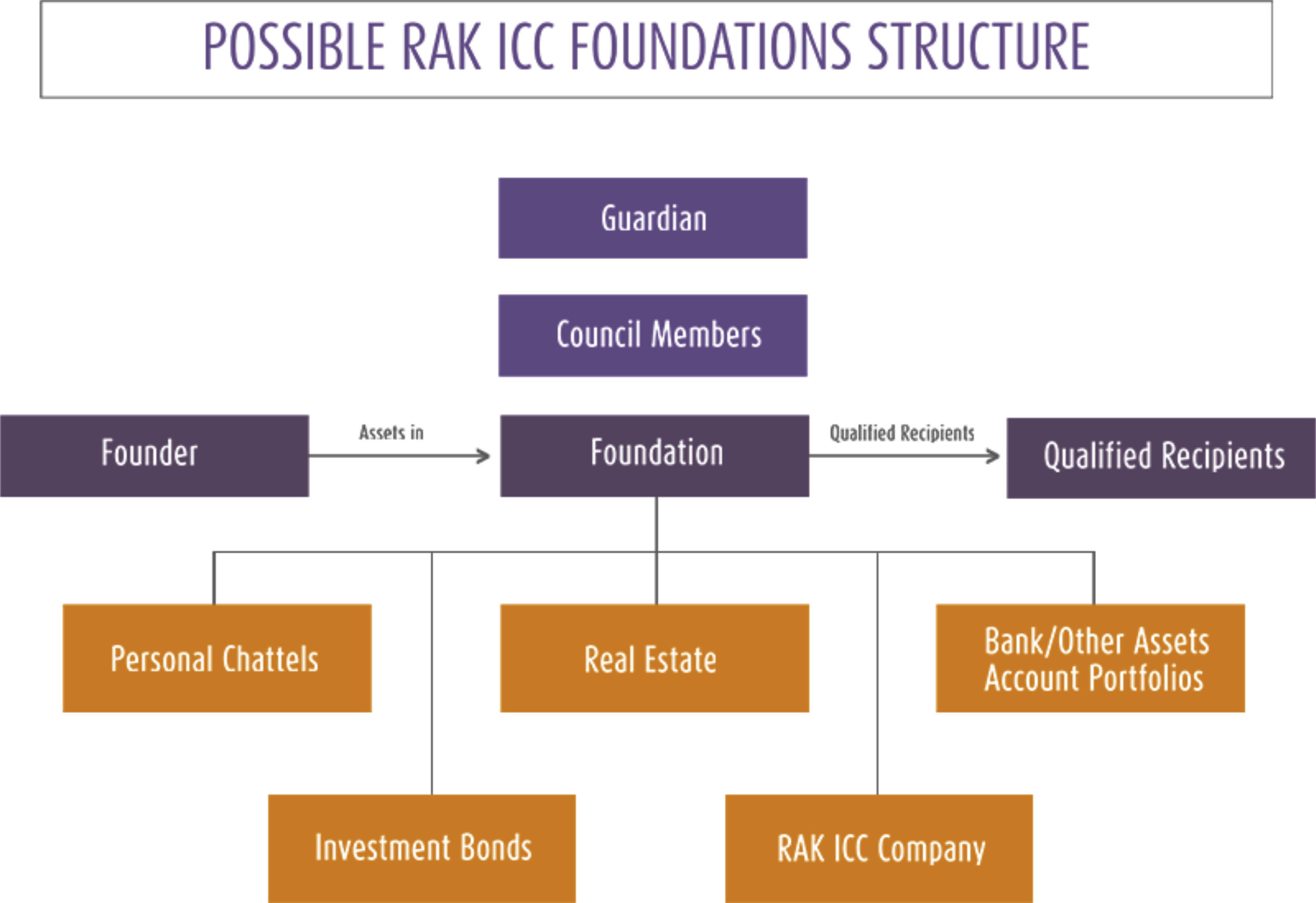

Overview of RAK ICC Foundations
Governing Law
The RAK ICC Foundations Regulations 2019.
Governing Jurisdiction
A choice of common law jurisdictions between either: The Courts of the Abu Dhabi Global Market; or The Courts of the Dubai International Financial Centre.
Governing Jurisdiction
One may select between two distinguished common law jurisdictions: the Courts of the Abu Dhabi Global Market or the Courts of the Dubai International Financial Centre.
Language
English
Incorporation Procedure
Criteria for the incorporation process is as follows:
- A Founder (Individual or Body Corporate)
- A Council Members (Individual or Body Corporate)
- A Registered Agent
- A UAE Registered Office
A Foundation that pursues a charitable object or a specified non-charitable object is required to appoint a Guardian (Individual or Body Corporate). To proceed, the Application Form must be completed and signed by the Founder. This form must subsequently be submitted to the Registrar, accompanied by the relevant details, the Charter, and the By-Laws.
Minimum Capital
USD 100 (or its equivalent in any other currency).
Additional Property may subsequently be contributed to the Foundation by a Contributor.
Control Mechanisms
The Foundation is led by the Council Members who operate under the Framework of the By-Laws, a crucial private document that guides our governance.
The Council is composed of a minimum of two Members, who may include the Founder, Family Members, Trusted Advisors, or Professional Advisers, whether as individuals or as corporate entities. The Guardian, if appointed, is responsible for supervising the Council Members and ensuring their strict compliance with the By-Laws of the Foundation.
Right to Information
The Registrar will uphold a Foundations Register that captures vital information for each Foundation, including the Name, registration date, Founder details, Council Members, and Registered Agent. All other information is deemed confidential and will only be shared when mandated by the appropriate authorities.
Migration
Migration of a Foundation into, or from the RAK ICC, is permissible subject to certain conditions.
Annual Accounts
The registered agent shall maintain the accounting records at the registered office. The accounting records are not subject to public disclosure.
